Gas Storage Class
| Description: | storage where gas can be injected and extracted |
| Detail: |
See also Gas Storage Property Reference for a detailed list of properties for this class of object.
See the Gas Modelling article for details.
A Gas Storage connects to the gas network via the Gas Node membership.
Unlike electricity, natural gas benefits from its ability to be stored.
Gas is injected into storage during periods of low demand and withdrawn from it during peak demand. This is important for balancing the flow in pipeline systems, ensuring against unforeseen accidents, meeting regulatory obligations, and for other strategic purposes. The main storage types, each with distinct physical and economic characteristics, are:
- Depleted gas reservoirs
- Aquifer reservoirs
- Salt cavern reservoirs
- Man made gas storage tanks
Gas storage requires a certain level of saturation before one is able to withdraw natural gas. This level is known as base gas. In PLEXOS this is denoted as Min Volume.
Working gas is the amount of natural gas greater than the base gas. In PLEXOS, working gas is the difference between Max Volume and Min Volume.
Note: Two types of injection/withdrawal ratchets are offered - volume based, or percent volume based.
Gas Storage
Gas storage is principally used to meet load variations. Gas is injected into storage during periods of low demand and withdrawn from storage during periods of peak demand. It is also used for a variety of secondary purposes, including:
- Balancing the flow in pipeline systems
- Maintaining contractual balance
- Leveling production over periods of fluctuating demand
- Insuring any unforeseen accidents
- Meeting Regulatory obligations
- Reducing price volatility
The Gas Storage object's obligatory membership is with "Gas Node".

Production
The key property to toggle the "Gas Storage" object on and off of the optimization is the "Max Volume" property. It can be set off as zero in case the user wants to deactivate the Gas Storage object.
The amount of Max or Min volume of gas allowed in the storage can be adjusted by the "Max Volume" and "Min Volume" property, respectively. For gas storage capacity expansion, the Expansion Max Volume can be defined to set a maximum on expansion volume.
End Effects Method
Gas Storage "End Effects Method" controls the method used to value or constrain the Final End Volume of each simulation step. The setting can take the following options:
- Free - End Volume is set freely by the optimization. In other words, no additional value or constraint is placed on this value.
- Recycle - The End Volume is constrained equal to the Initial Volume of the simulation step. This option adds a constraint to the simulation. The penalty for violating this constraint is by default -1 (indicating a 'hard' constraint). This can be changed with the setting Recycle Penalty.
Constraints
The injection-withdrawal level of gas in any interval can be constrained by the "Max Injection" and "Max Withdrawal" properties while "Target" property sets the end-of-interval target for the End Volume. This target will set every interval of the simulation and it can be associated with a penalty that makes this constraint soft.
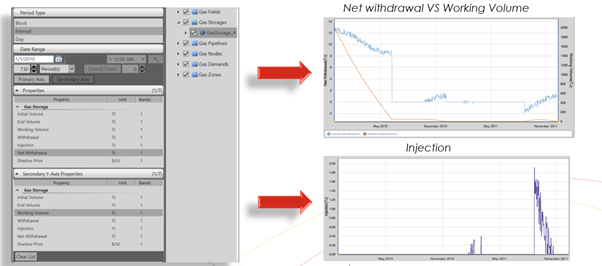
Reporting
A variety of output properties could be enabled from the reporting menu such as "Net withdrawal", "Working Volume", and "Injection".