Nodal Radial Equivalence
The radial equivalency feature potentially reduces nodal problem size and speed of solution by eliminating radial lines within a loadflow case.
Using the Equivalence Radials function eliminates the radial lines within a loadflow case, at the same time preserving all of the network data required to reproduce the LMP results of the original case. The process includes accounting for losses in the processing of demand buses and does not roll up radial systems with generators with average maximum capacity exceeding 50 MW.
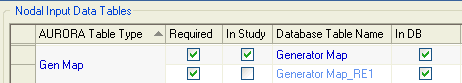
The process automatically reassigns load and generators from eliminated radial buses to equivalent buses that remain in the system and creates a new Generator Map table to preserve the relationships between Aurora resource IDs and the newly configured loadflow generators in the equivalenced case. A log of the changes is written to a text output file.
![]() NOTE: The process will use the data tables selected for use in the study for the Generator Map table and Supplemental Bus tables, so before starting the process be sure that those tables correspond to the loadflow case that is to be converted.
NOTE: The process will use the data tables selected for use in the study for the Generator Map table and Supplemental Bus tables, so before starting the process be sure that those tables correspond to the loadflow case that is to be converted.
After selecting the menu item the user will be prompted to select a loadflow case file (extension = .alfc) to equivalence and to create a file name to store the new case. A sequence of messages similar to the set below is displayed in the Status Window, showing the input case, the output case, the new Generator Map table, and the bus reduction count.
Nodal Info: Beginning radial equivalence of alfc file 'C:\AURORAxmp\Nodal_10Bus_Example.alfc'.
Nodal Info: Network definition file 'C:\AURORAxmp\Nodal_10Bus_Example.alfc' read.
Nodal Info: Radial equivalence finished with bus reduction count = 1
Nodal Info: New GenMap table 'Generator Map_RE1' created from table 'Generator Map' and placed in input DB.
Nodal Info: Radial equivalence completed for case file 'C:\AURORAxmp\Nodal_10Bus_Example.alfc'. Result stored in file 'C:\AURORAxmp\Nodal_10Bus_Example_RadEqv.alfc'.
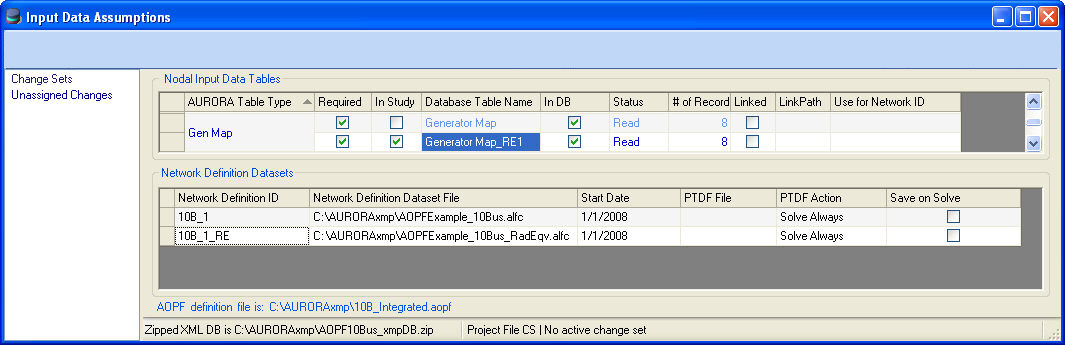
The new Generator Map table is named after the original map table, but with an “_REn” appended, where "n" is the first integer producing a unique table name. (e.g. in the example shown below “Generator Map” is used to create “Generator Map_RE1”.)
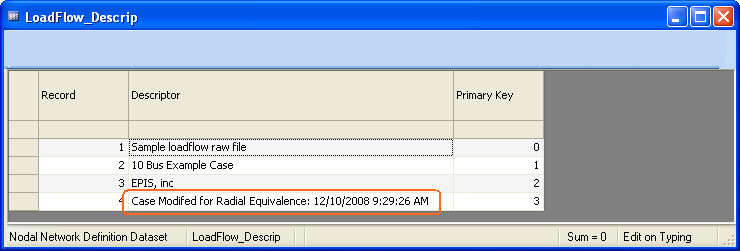
In addition, a new record is added to the duplicate LoadFlow_Descrip table annotating the equivalence.
![]() NOTE: Other Nodal Input Data tables are not modified by the radial equivalency. A warning will occur if records in these tables are affected and they will need to be modified by the user to conform to the equivalenced case.
NOTE: Other Nodal Input Data tables are not modified by the radial equivalency. A warning will occur if records in these tables are affected and they will need to be modified by the user to conform to the equivalenced case.
A log file, that holds information showing which buses are rolled into a radial bus and new names and bus locations for any generators that were on an eliminated bus, is written to the same file path where the Aurora Messages.logMessages.log is written. The file name will start with “xmpRadialEquiv” and end with a time stamp denoting time of file creation. A new file is created each time a radial equivalence is performed. The log file is a standard text file that can be viewed with any text viewing application.
Once a case has been equivalenced it can be used by adding a row to the Network Case grid. The newly created Generator Map table, corresponding to the equivalence case, must be manually selected for inclusion in the study.
![]() Equivalence Radials
Equivalence Radials
